Intelligent construction, or "smart building", refers to a new construction concept that uses innovative design, construction and system solutions aimed at minimizing energy dispersion and guaranteeing high standards of efficiency. In a smart building, all elements are interconnected and communicate in real time to ensure maximum comfort, safety and health of occupants. This type of construction places emphasis on environmental sustainability, energy saving and on the quality of life of the occupants.
Why is it important?
To face the ever-increasing phenomenon of climate change, governments and institutions worldwide have established a shared plan to reduce CO2 emissions by 55% by 2030 compared to the 1990 level. This strategy also includes objectives to increase the share of renewable energy in the EU and improve energy efficiency. According to the World Research Institute in 2016, 5.5% of global emissions came from the Real Estate sector (this percentage rises to 17.5% at end use level). Even the most recent data confirm this trend: it is therefore immediately clear that policies that promote the energy efficiency of buildings can contribute to better achieving the objective of reducing these emissions.
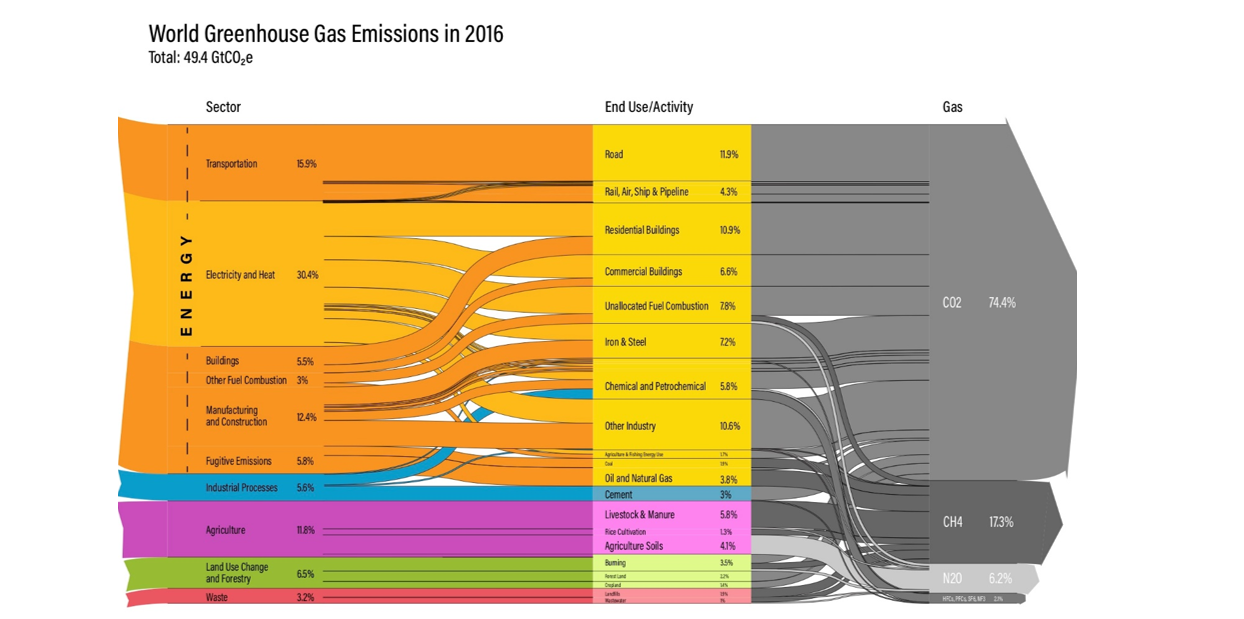
Figure 1. Source: World Research Institute, Climate Watch, 2016
Actual scenario
The latest research from the European Commission shows that the European construction sector is made up of 73% residential buildings and 27% non-residential (commercial/industrial).
Figure 2. Source: European Commission, Morgan Staley Research
In terms of energy consumption, the construction sector consumes approximately 42% of energy: in detail, in the residential sector, only 20% of this energy comes from renewable sources. Heating and cooling represent the largest component of energy consumption (63%).
Energy consumption by sector; energy consupmtion in the residential sector by fuel; energy consumption in the residential sector by activity, Europe 2020
Figure 3. Source: Eurostat, BofA GLOBAL RESEARC
Today, Europe annually renovates only around 1.4% of the residential building stock and 1.7% of the non-residential building stock (weighted energy renovation rate meaning the annual reduction of primary energy consumption). Of these renovation interventions, only a small part (0.2%) are interventions that allow medium/high energy savings (i.e. they allow a saving of at least 60% in energy consumption). Climate goals therefore require an extremely ambitious wave of “renewal” that accelerates the quantity and quality of such interventions. Doubling the renovation rate to around 3% (according to the Commission's ambition) implies renovating Europe's building stock in 33 years rather than the current path of around 70 years.
In a scenario where renovation spending rises to meet the green investment gap required to deliver the renovation wave, construction spending could average 3%, well above the historical long-term average.
Figure 4. Source: Morgan Stanley research estimates, European Commission
Main Technologies in Smart Buildings
Technologies used in smart buildings include Building Management Systems (BMS) and digital and management applications. These technologies, thanks to the integration and control platforms, are able to interact and integrate with systems and products inside the building.
The advantages of sustainable smart building are numerous: from reducing energy consumption to reducing pollution, from improving comfort to safety:
- Consumption control and monitoring: thanks to the use of sensors and intelligent control systems, it is possible to monitor the building's energy consumption in real time and optimize its operation.
- Reduction of CO₂ emissions and energy costs: a sustainable building is able to reduce its CO₂ emissions, thus contributing to the fight against climate change and allowing significant economic savings to be achieved.
- Widespread connectivity: smart technologies allow all the elements of the building to be connected together, from sensors to systems, thus allowing integrated and intelligent management of different functions.
- Improvement of comfort: smart technologies can help maintain a comfortable environment inside the building, adapting the temperature and humidity inside the spaces based on the needs of the occupants.
- Security: smart technologies can help ensure security within the building, monitoring spaces and reporting any anomalies.
- Innovative materials for thermal insulation
- Intelligent sensors and control systems
- LED lighting systems
- Heat pump heating/cooling systems
Impacts
According to estimates from the European Commission, every year in Europe 275 billion euros of additional investments will be needed in building renovation between now and 2030, or around 2,800 billion which will become over 5,000 if the horizon is extended to 2050. This implies a doubling of growth rates in spending on building renovation (currently stuck at rates around 1.5%/1.7%).
In terms of individual businesses linked to building renovation, main surveys conducted in 2022 on spending intentions for interventions for the next year highlighted good growth opportunities on insulation materials (35% of respondents planned interventions of this type, compared to 27% in the previous year), automation and control systems and cooling/heating systems.

Figure 5. Source: Alphawise, Morgan Stanley Research, Eurizon Capital SGR elaboration
Disclaimer:
Nothing in this document is intended as investment research or as a marketing communication, nor as a recommendation or suggestion, express or implied, with respect to an investment strategy concerning the financial instruments managed or issued by Eurizon Capital SGR S.p.A.. Neither is this document a solicitation or offer, investment, legal, tax or other advice.
The opinions, forecasts or estimates contained herein are made with reference only to the date of preparation, and there can be no assurance that results or any future events will be consistent with the opinions, forecasts or estimates contained herein. The information provided and opinions contained are based on sources believed to be reliable and in good faith. However, no representation or warranty, express or implied, is made by Eurizon Capital SGR S.p.A. as to the accuracy, completeness or fairness of the information provided.
Any information contained in the present document may, after the date of its preparation, be subject to modification or updating.










